文章目录
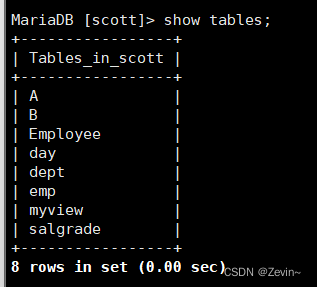
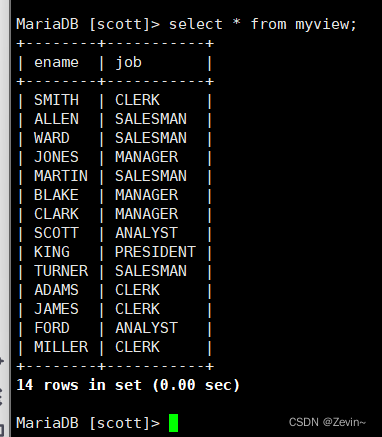
视图 视图是一个虚拟表,其内容由查询定义,同真实的表一样,视图包含一系列带有名称的列和行结构
把查询的结构形成一个新的表
1 create view myview as select ename,job from emp;
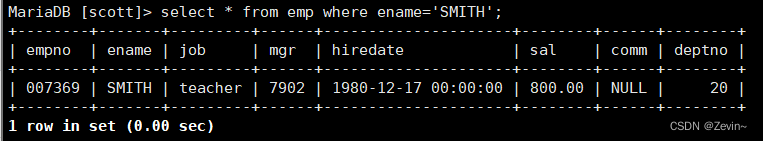
我们在修改myview里面的数据的时候,其实就是对原始表的数据进修修改
1 update myview set job= 'teacher' where ename= 'SMITH' ;
这个表就相当于做了一个中间的媒介
用户管理 如果我们每次都只能使用root,这样会存在安全隐患,这是,就需要使用MySQL的用户管理
用户管理都在一张表里面
host:代表这个用户可以从哪个主机登录user:用户名authentication_string:用户密码通过password函数加密之后*_priv:用户拥有的权限
如何增加普通用户 创建用户同时设置密码
1 create user 'xzw' @'127.0.0.1' identified by '12345678' ;
登录
如何删除普通用户 如何给用户赋权 grant 权限列表 on 库,to对象名
1 grant select on 102 db.* to xzw@'%' ;
给这个用户添加一个select权限
grant all 添加所有权限,设置所有权限
1 grant all on * .* to 'username' @'hostname' ;
如何给用户取消权限 revoke from对应添加权限里面的grant 和to
1 revoke all on * . * from test_db @'%' ;
删除用户 这个比较明确
1 drop user username@'hostname' ;
刷新 修改完数据之后,要刷新一下
图形化 使用图形化界面来访问MySQL
MySQL workbench +Windows(mysql):不跨网络
MySQL workbench+Linux(mysql):跨网络(比较仿真的),不太完全的,配置端口号,把root密码设计复杂
开放端口才能链接上网络
我们从官网下载的安装包
C语言连接MySQL 1 2 ln -s ~/mysql-connector-c-6.1 .11 -linux-glibc2.12 -x86_64/include include-6.1 .11 -linux-glibc2.12 -x86_64/lib lib
编译
1 2 mysql:test.ccstd =c++11 -I./include -L./lib -lmysqlclient
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 #include <mysql/mysql.h> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> using namespace std;int main () "client version: " <<mysql_get_client_info ()<<endl;return 0 ;
1 MYSQL *my = mysql_init (nullptr );
1 mysql_real_connect (my, host.c_str (), user.c_str (), password.c_str (), db.c_str (), port, nullptr , 0 );
1 mysql_set_character_set (my, "utf8" );
所有对数据库的操作都是使用这一个函数进行操作
1 int res = mysql_query(my, sql.c_str()); / / 执行数据库操作,成功返回0 ,失败返回1
1 MYSQL_RES* result=mysql_store_result (my);
1 2 int rows=mysql_num_rows (result);int cols=mysql_num_fields (result);
1 MYSQL_FIELD* field=mysql_fetch_field (result);
1 2 3 4 for (int i=0 ;i<cols;i++)"\t" ;
打印数据库里面的每个数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 for (int i=0 ;i<rows;i++)mysql_fetch_row (result);for (int j=0 ;j<cols;j++)"\t" ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 #include <mysql/mysql.h> #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <string> using namespace std;"127.0.0.1" ; "root" ; "@xzw108858!!" ; "db1" ; int port = 3306 ;int main () "client version: " << mysql_get_client_info () << endl;mysql_init (nullptr );if (mysql_real_connect (my, host.c_str (), user.c_str (), password.c_str (), db.c_str (), port, nullptr , 0 ) == nullptr )"connect fail" << endl;return 1 ;mysql_set_character_set (my, "utf8" );"connect success" << endl;"select * from myclass where room=\'ds\'" ;int res = mysql_query (my, sql.c_str ()); mysql_store_result (my);if (res)"faliue" << endl;int rows=mysql_num_rows (result);int cols=mysql_num_fields (result);"行数=" <<rows<<"列数=" <<cols<<endl;mysql_fetch_field (result);for (int i=0 ;i<cols;i++)"\t" ;for (int i=0 ;i<rows;i++)mysql_fetch_row (result);for (int j=0 ;j<cols;j++)"\t" ;free (result);mysql_close (my);return 0 ;